What is a VPN and how it impacts online security
1Click VPN Team in cybersecurity
07.12.2023 | 4 min read

Table of contents
VPN stands for virtual private network, which refers to a system of placing a ‘middleman’ server between the internet user and the browser on their connected device. In a typical setup where a user is not accessing the internet via a VPN, the connection works like this:
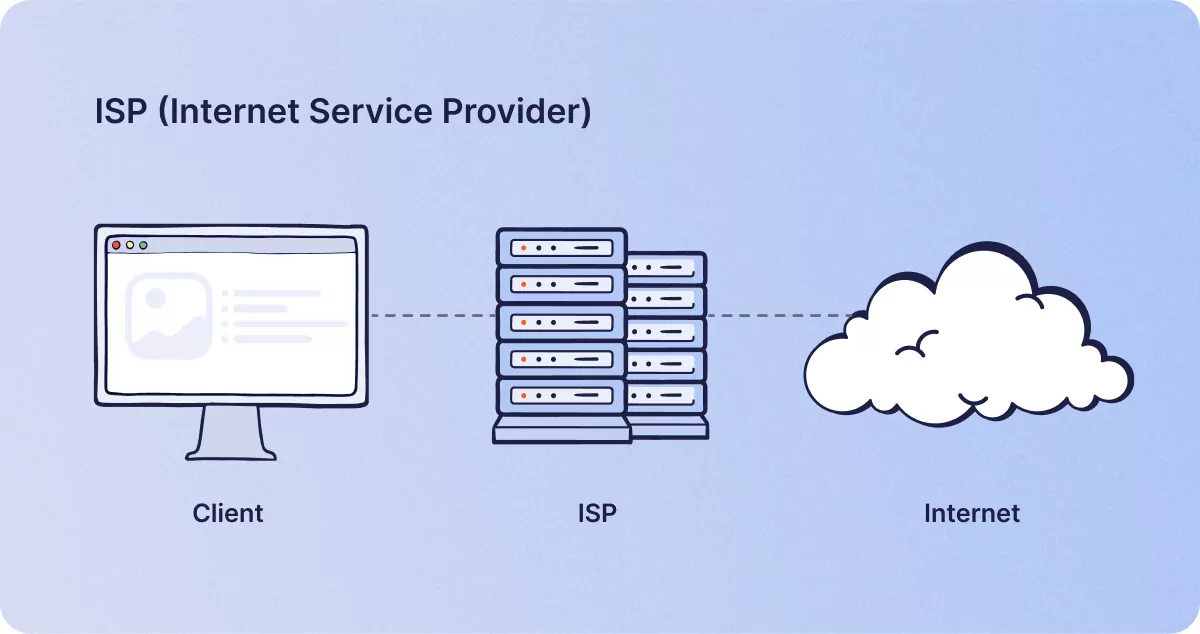
The user’s home router connects to their internet service provider’s (ISP) server and that server looks up the IP (internet protocol) address of the user’s desired target website. It’s important to remember that IP addresses are in fact numerical because it’s easier to remember and type in the words Google.com than the IP 172.217.6.196, for example. Here’s a super simplified illustration of how ISPs works.
So the internet user connects to their IP via the router, and the ISP in turn allows the connection to the target website. The user‘s browser then converts all that hypertext into an understandable language, say US English, and the session continues. The ISP can keep a log of who the connected customer is, how long they visited the internet, which sites they visited, how many emails they sent and received, and lots of other personal information.
However, if a person uses a VPN, then the VPN software creates an encrypted ‘tunnel’ to a server in its own network, which acts as an intermediary between the user and their ISP. Crucially, because this intermediate server is encrypted, the ISP’s server can’t tell who is making the connection request, nor indeed, where they are based. This geo-location scrambling is one of the major advantages to using a VPN, for reasons we’ll expand upon below; but suffice to say that the VPN user can choose a server anywhere in the world from where to access the web.
This anonymity and location independence offer several advantages when using the internet; let’s take a look at some of the most common factors and why they offer such utility:
Secure Remote Access
VPNs are often employed by organizations to allow remote workers to secure access to company networks from wherever they might be. With the post-Covid 19 work from home (WFH) culture, this has become especially useful as many knowledge workers in white-collar roles can work from any location. However, many companies are understandably nervous if an employee logs on from a free Wi-Fi network somewhere in a shopping mall or vacation hotel. Companies usually insist that their workers use an organizationally-approved VPN to log onto their workplace accounts. This can help to protect sensitive corporate data no matter where it is being accessed from.
Public Wi-Fi networks, found in coffee shops, airports, and malls are usually less secure than home or office networks for easy accessibility, but this makes them an easier target for cyberattacks. A VPN secures any connection on such networks, thereby allowing users to enter credit card details and passwords without them being stolen by cyber-criminals. Any hacker with even the most cursory knowledge can break into another person’s computer via a free Wi-Fi network, but a VPN again provides an encrypted gateway between the device and the network to which it is connected.
Data Throttling
The practice of ‘data throttling’ is more common than you might think. It involves the simple slowing down of data transfer between an ISP’s customer and a given website or online service. The ISP does this because they don’t have truly unlimited bandwidth and if, say, 90% of all their customers decided to stream an Apple TV show all at the same time (as can happen when new series are released) then their network could be overwhelmed. ISP’s use algorithms to predict who is most likely to access a certain data-hungry service and can slow down (throttle) either individual customers or even entire suburbs in line with load demands.
Furthermore, some ISPs are very crafty about hiding the fact that they carry out this activity, by ensuring that the IP addresses of popular ‘speed test’ sites remain unthrottled. In that case, a typical scenario might be that an ISP customer finds their Apple TV streaming badly ‘buffered’ – visits a site like ‘speedtest.net’ and finds that their internet speed appears to be as promised in their contract. So they blame the streaming service provider rather than their ISP.
But by using a VPN, the ISP can’t identify the user, nor even where they are, so it’s impossible for them to ‘throttle’ that particular connection.
Access geographically restricted content
Furthermore, the fact that a VPN user can choose from perhaps hundreds of worldwide access points to visit the internet can circumvent geographic restrictions on content. A good example of this is the UK’s BBC iPlayer service, from which viewers can see almost the entirety of the BBC’s output at any time 24/7/365. It’s common knowledge that the BBC’s once trusted news service (before the corporation became a puppet for a succession of right-wing Tory governments over recent years) was accessed by students from Hong Kong during the time when China repressed that colony. But without a VPN, accessing the BBC iPlayer from China is impossible. The iPlayer’s technology detects the location of the visitor and blocks their access – the service is available to UK license payers only.
However, if someone in China uses a VPN to access the internet, they would only need to choose a UK-based server from the VPN’s list, and within moments they would be connected to BBC content. Such was the repression of the Chinese authorities over such matters, that using a VPN was illegal without permission, and stiff penalties were doled out to transgressors.
Likewise, on a less serious level, if you’re traveling on vacation in France and you normally live in the USA – you can catch up on your favorite Netflix show by choosing a VPN server in Paris Texas, rather than Paris France!
These are just three of the advantages of using a VPN, others include the avoidance of IP logging by your ISP, the circumvention of dynamic pricing (whereby online retail customers are charged higher prices because they live in wealthy areas), and advanced protection against malware and phishing attacks. Also, your ISP can’t sell your anonymized data to advertisers; many people think that if ISPs are going to make money out of customer data, they’d like a percentage of the proceeds – it’s not an unreasonable point of view.
Finally, it’s important to remember that a VPN can help with security, but their effectiveness varies by provider. VPNs aren’t a cure-all for online security, so a belt-and-braces approach should be taken, with up-to-date virus protection on devices and retention of strong passwords; it’s essential to combine VPN usage with other usual strong cybersecurity practices.
Similar posts

Test your VPN – How to check if a VPN is working
Virtual Private Networks have quickly become go-to tools for modern Internet users who are conscious of protecting their…

Staying Secure Online: 7 Tips for Safely Using Public Wi-Fi
The Internet is an essential part of virtually everything we do nowadays, from shopping to banking to entertainment, and…