Proxy Vs. VPN: What’s the Difference?
1Click VPN Team in cybersecurity
07.12.2023 | 3 min read

Table of contents
In an increasingly digital world, online privacy has become a major concern for Internet users the world over. As a result, proxies and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have emerged as two of the most widely utilized privacy solutions, with millions of users globally. But what exactly do VPNs and proxies do, and what differentiates them from one another?
In this blog, we’ll answer these questions, providing some context on how and when VPNs and proxies are utilized.
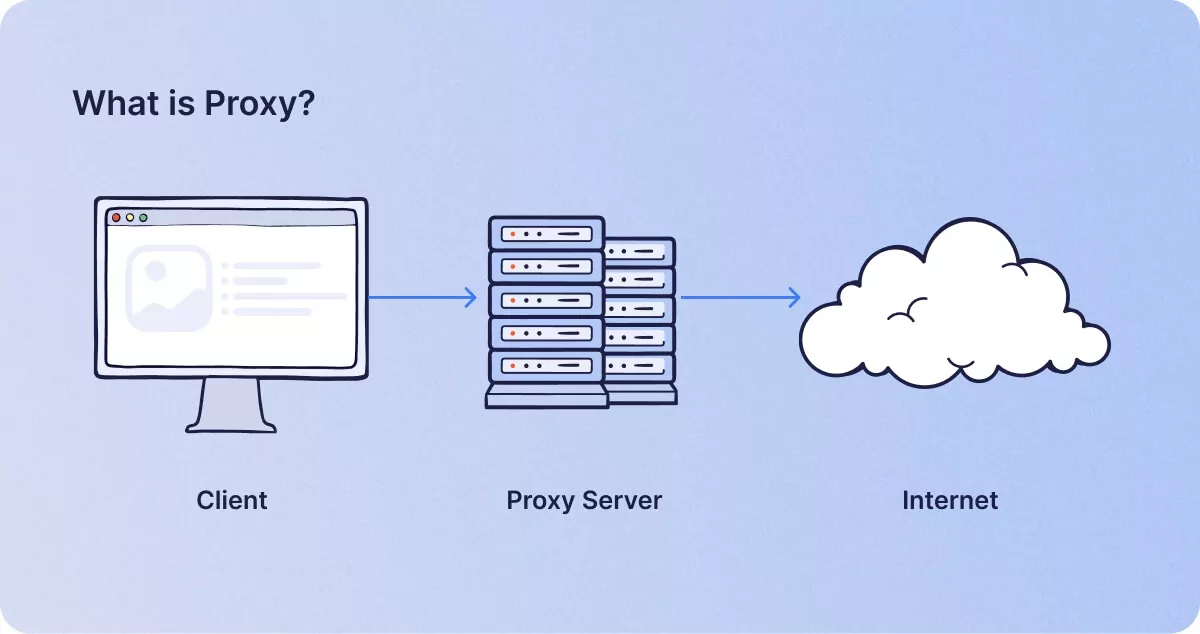
What is Proxy?
The term “proxy” refers to a server that is used to provide proxy services to users. Proxy servers act as gateways to the Internet by enabling users to establish a relay point between their devices and the sites they visit online. In doing this, users can maintain anonymity on the Internet by concealing their IP addresses and browsing under those of their chosen proxies.
Proxies can be dedicated, providing a single fixed IP for individual users, or shared, meaning that they are utilized by pools of different users concurrently. Both are widely used, but situational depending on the level of flexibility and IP continuity required by a user.
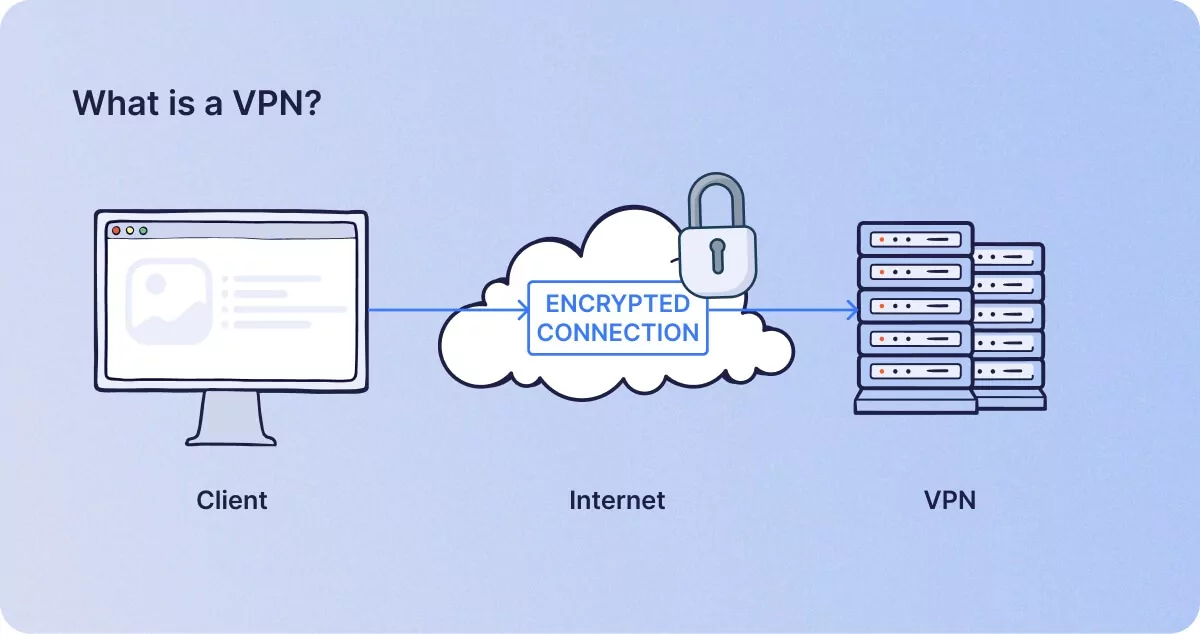
 What is a VPN?
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network, or VPN, is a combined privacy and security solution for Internet activity. In a similar manner to proxies, VPNs allow users to divert their Internet connections through remote servers. As with proxies, they enable users to conceal their IP addresses and locations in order to remain anonymous and bypass geographical restrictions.
However, there exists an important difference that separates VPNs from proxies: the use of encryption. When you connect to the Internet using a virtual private network, robust encryption protocols are applied to your device’s Internet traffic. This renders data packets unreadable to those who might intercept them, providing a greater degree of protection on networks without strict authentication.
As such, VPNs can be said to be the more effective option when it comes to cybersecurity.
Proxy vs VPN
Just as there exist notable differences in how proxies and VPNs work, so too do the two have slightly different use cases. The following are some of the most common use cases for proxies and VPNs:
Proxy Use Cases
- Bypassing Geo-blocks: As proxies allow users to simulate internet activity from other regions, they are useful for bypassing geo-blocks, which restrict access to sites or content based on user location.
- SEO Monitoring: Since proxies allow users to search from different regions and avoid geo-targeted results, they are useful for conducting searches and viewing SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages) to gain accurate insights into the SEO rankings and trends.
- Digital Ad Verification: Because proxies let users view web pages as people in other regions see them, they are useful for verifying digital ads intended for overseas audiences.
- Web Scraping: Proxies, specifically rotating proxies, allow users to switch between different IPs on a regular basis. This makes them useful for data collection, enabling data scraping on websites that would otherwise block IPs that send high volumes of data requests.
VPN Use Cases
- Accessing restricted Content: As with proxies, VPNs allow users to change their location when they go online. As such, they are useful for bypassing blocks to access specific online platforms and content, such as when traveling.
- Remote Work: Users who engage in remote routinely use open public networks to do so. Such networks are often unsecured, so VPNs are useful for safeguarding user devices on unprotected networks.
- Combatting ISP Throttling: Bandwidth throttling is a widespread issue, with ISPs (Internet Services Providers) routinely restricting data transfer speeds in response to high-bandwidth activities like streaming, gaming, or downloading. Since they conceal user IPs and encrypt traffic for maximum privacy, VPNs are useful for preventing issues with bandwidth throttling.
- Online shopping: Because VPNs allow users to change locations, they are suitable for aggregating product prices in different regions to avoid paying more during to dynamic pricing. Additionally, since they provide encryption to data traffic, VPNs offer a secure way to make purchases online by protecting sensitive data provided during digital transactions.
The above are just some of the most common use cases for proxies and Virtual Private Networks. Due to their considerable utility in different situations, both technologies have a wide variety of use cases, both private and commercial. Broadly speaking, however, we can say that while both proxies and VPNs are useful for tasks that require anonymity and locational flexibility, VPNs are the more appropriate choice in instances where cybersecurity and data protection are key concerns.
Conclusion
In today’s digital landscape, privacy is a constant priority whenever we go online, whether it is for personal or business purposes. This need for privacy has created a thriving niche in the tech space, with VPNs and proxies presenting viable ways for users to protect their identities and circumvent issues stemming from geo-based restrictions. While there is considerable overlap in the functionality of VPNs and proxies, however, it is important to note the differences. For instance, while the former places a much greater emphasis on security, specifically by applying strong encryption to user data, the latter offers a high degree of flexibility for tasks that necessitate regular IP changes.
All in all, both proxies and VPNs are extremely useful for protecting your privacy online, and both have their own niche use cases. Ultimately, the decision to opt for one or the other will depend on your specific situation, objectives, and needs.
Similar posts

Why some countries block WhatsApp and how to unblock it
Why do some countries block WhatsApp? As in so many walks of life, one of the primary reasons for governments doing anyt…

Test your VPN – How to check if a VPN is working
Virtual Private Networks have quickly become go-to tools for modern Internet users who are conscious of protecting their…
 What is a VPN?
What is a VPN?